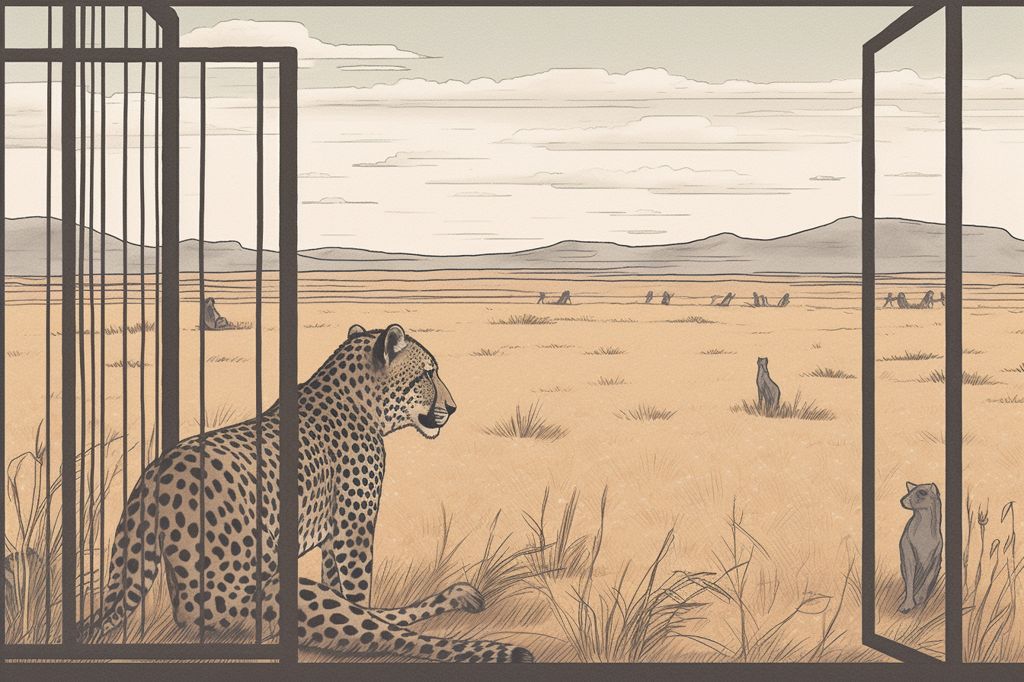
The reintroduction of cheetahs to their former range in India is a complicated and perilous process that requires careful monitoring and management. The Memorandum of Understanding signed between South Africa and India aims to promote cooperation and shared expertise for the conservation of cheetahs. However, the recent death of one of the 12 cheetahs relocated to Kuno National Park has highlighted the significant challenges of the reintroduction project, particularly during the critical phase of releasing cheetahs into free-ranging conditions.
Risk of Injury and Mortality
The death of the cheetah is currently under investigation, but there is no indication that it was caused by an infectious disease, nor is there any similar threat to the other cheetahs. However, the risks of injury and mortality increase as more cheetahs are released into larger environments with less control over their daily wellbeing.
Threats to Survivability
Kuno National Park is home to a high density of competing predators, including leopards, wolves, sloth bears, and striped hyenas, posing a threat to the cheetahs’ survival. It is anticipated that some of the founder population may be lost within the first year post-release, as observed with cheetah reintroductions in Africa.
Escape and Recapture
Many of the released cheetahs are likely to escape the boundaries of Kuno National Park, requiring them to undergo stress during the recapture process. However, once they establish their home ranges, the situation is expected to stabilize.
Collaboration for Conservation
The collaboration between South Africa and India under the MoU is a significant step towards establishing a viable and secure cheetah population in India and promoting cheetah conservation. The reintroduction of cheetahs to India is a complex and risky process that requires careful monitoring and management. The recent death of one of the relocated cheetahs underscores the challenges of the project, particularly during the critical phase of releasing cheetahs into free-ranging conditions. However, the collaboration between South Africa and India under the MoU is a positive step towards the goal of establishing a viable and secure cheetah population in India and promoting cheetah conservation.