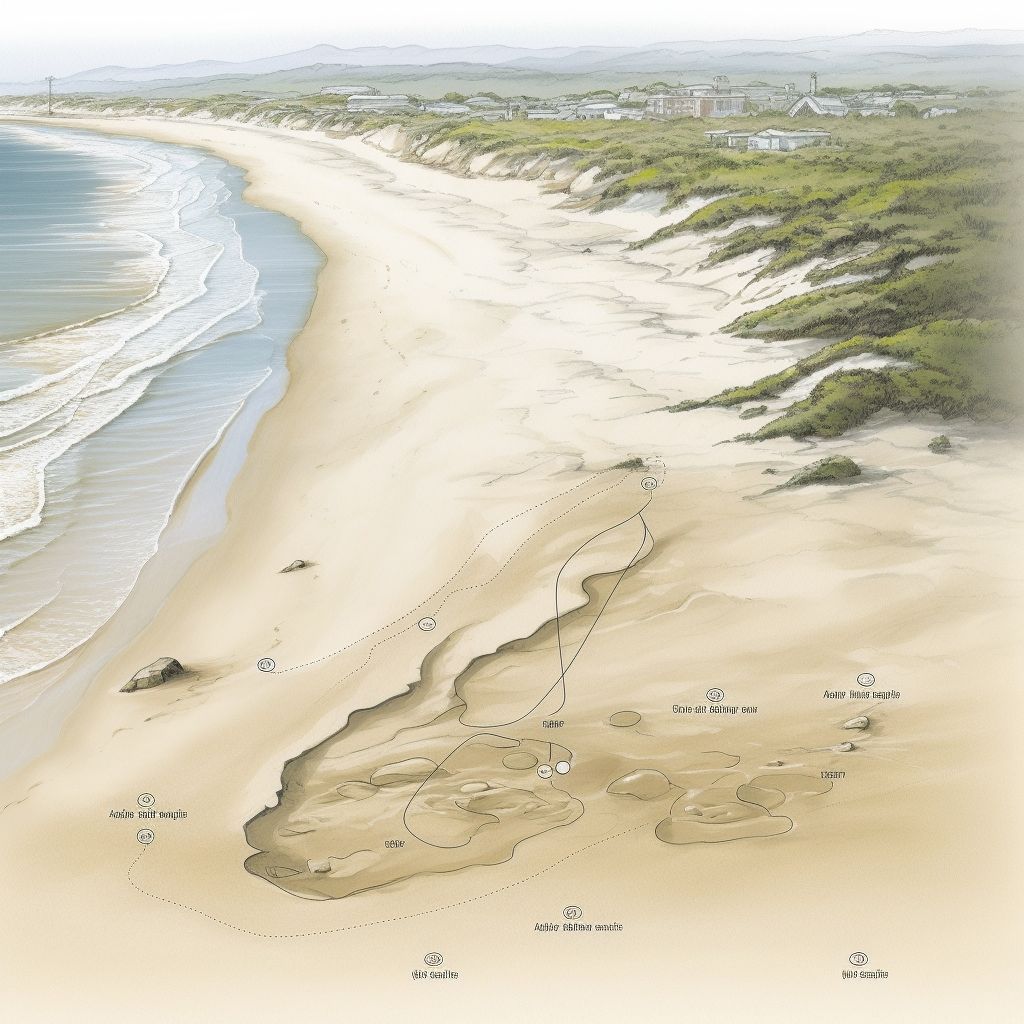
South Africa’s Cape south coast has recently revealed an extraordinary discovery, providing significant insight into our human ancestry. The world’s oldest Homo sapiens footprint, dating back 153,000 years, was found in the Garden Route National Park, west of the coastal town of Knysna. This footprint outdates the previously known South African sites of Nahoon (124,000 years) and Langebaan (117,000 years).
Increasing Exploration of Hominin Ichnosites
Only recently, only four African sites contained tracks older than 50,000 years. However, due to increased exploration, the number of dated hominin ichnites has risen to 14. These sites are divided into the East African cluster of five locations and the South African group from the Cape Coast, with nine areas. Ten additional sites have been found worldwide, including in the UK and the Arabian Peninsula.
Significant Insights into Early Humans
The ichnites offer invaluable insights into the lives of our ancient ancestors, as skeletal remains on the Cape Coast are scarce. In addition, the findings contribute to understanding how early anatomically modern humans evolved and thrived in Africa before migrating to other continents. In a recent article published in Ichnos, the international journal of trace fossils, seven newly dated hominin ichnites along South Africa’s Cape south coast were revealed, dating from 153,000 to 71,000 years ago.
Differences between East and South African Ichnosites
Fascinatingly, the East African and South African clusters exhibit significant differences. The East African sites, which date back to 3.66 million years ago, were formed by earlier species such as australopithecines, Homo heidelbergensis, and Homo erectus. In contrast, the South African sites are much younger, attributed to Homo sapiens, and the tracks are typically found fully exposed on rocks known as aeolianites.
Identifying the Age of Ancient Sediments
The optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) method is employed to determine the age of these ancient sediments, measuring the duration since a grain of sand was last exposed to sunlight. Since the tracks were formed by impressions in wet sand, OSL provides a reasonably accurate estimate of the sediment’s age. The Cape South coast is a suitable location for applying OSL, as its abundant sunshine, expansive beaches, and wind-transported sand create favorable conditions for accurate age estimates.
Pursuing More Discoveries
The African Centre for Coastal Palaeoscience research team at Nelson Mandela University in Port Elizabeth continues its pursuit of unearthing more hominin ichnites along the Cape South coast and beyond. The search should extend to deposits ranging in age from 400,000 years to over 2 million years. In a decade, the list of ancient hominin ichnites is expected to be much longer, providing further insights into our ancestors’ lives and the landscapes they inhabited.
Understanding Our Human Ancestry
The discovery of the 153,000-year-old footprint is a testament to the invaluable information hidden within the earth’s surface. Furthermore, it underscores the importance of continuing to search for more discoveries to understand the past better and enrich our comprehension of our ancient origins.