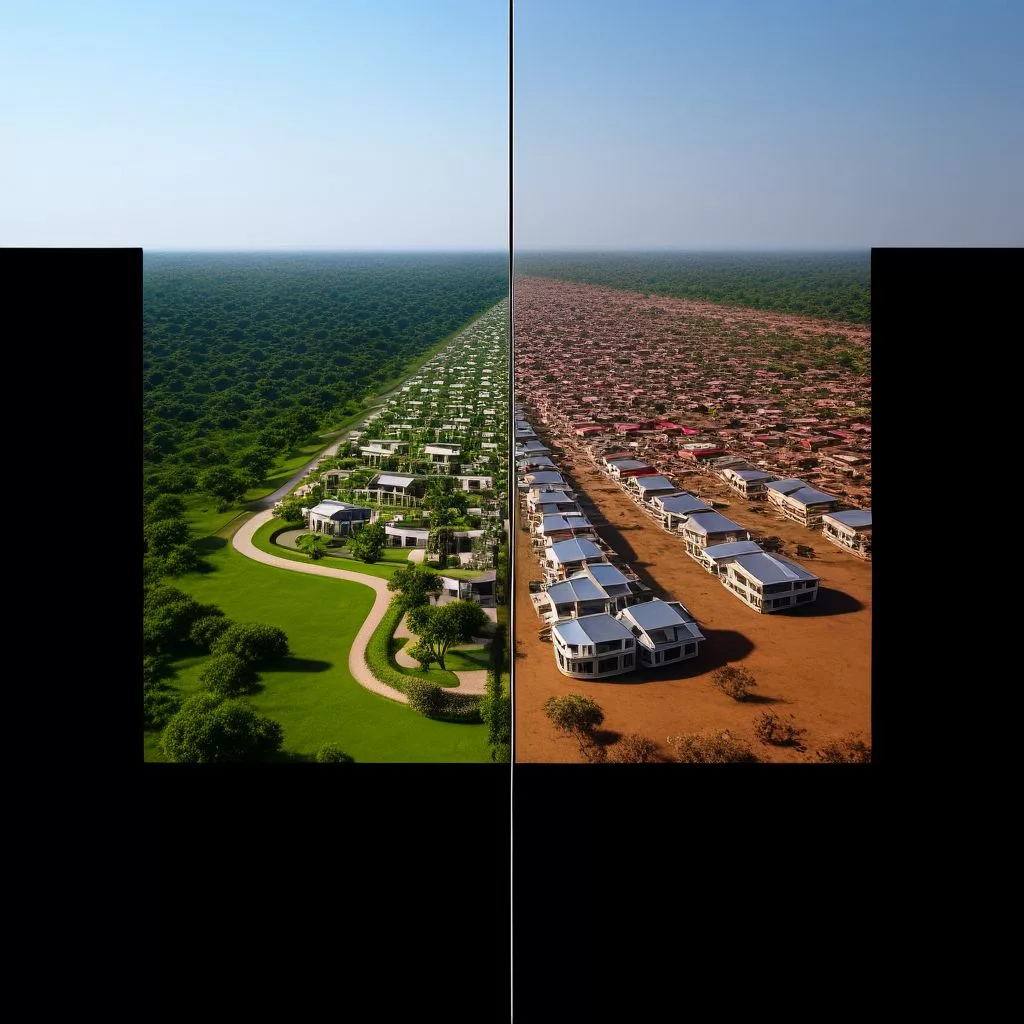
The Expropriation Act of 2024 is a big step in South Africa’s journey to fix past land injustices. It allows the government to take land for the “public interest,” meaning it can be used to help everyone, not just a few. This law also introduces the idea of paying no money for certain lands that are unused or abandoned, aiming to transform these spaces into thriving communities. While many people support this change, others worry about how it will work in practice. Overall, the Act shines as a hopeful sign for a fairer future in land ownership.
What is the Expropriation Act of 2024 in South Africa?
The Expropriation Act of 2024 is a significant land reform legislation that expands grounds for expropriation to include ‘public interest.’ It aims to address historical injustices, promote equitable land distribution, and allow for ‘nil compensation’ under specific circumstances, ensuring land serves the public good.
The Expropriation Act of 2024 has become a focal point for intense debate in South Africa, eliciting both enthusiastic support and strong opposition. This landmark legislation marks a departure from its 1975 predecessor by broadening the grounds for expropriation to include not just ‘public purpose’ but also ‘public interest.’ This expanded scope is designed to address historical injustices and lay the groundwork for more equitable land distribution, making it a significant step in the country’s ongoing journey towards land reform.
Historical Context and Legal Evolution
To fully grasp the transformative nature of the 2024 Expropriation Act, it’s essential to understand its historical and legal context. The 1975 legislation primarily served state interests, often ignoring the need for social equity and justice. It was a tool wielded without much regard for addressing societal inequalities. In stark contrast, the 2024 Act aligns with the principles enshrined in South Africa’s Constitution, particularly Section 25, which emphasizes land reform and equitable access to resources. This section provides a broad definition of property, encompassing both immovable and movable assets, yet it is the land issue that generates the most heated discussions.
South Africa’s pursuit of land reform stems from a compelling need to redress persistent social and economic disparities. The legacy of dispossession and disenfranchisement has left deep scars, fueling anger and resentment. The Expropriation Act of 2024 is poised to be a crucial instrument in healing these historical wounds. However, its effectiveness hinges on the state’s ability to implement the law in a fair and balanced manner.
Key Provisions and Controversies
One of the most talked-about features of the 2024 Act is its provision for expropriation with ‘nil compensation’ under certain circumstances. While this concept has sparked controversy, it is not entirely unprecedented. The previous legal framework, alongside the Constitution’s Section 25(3), allowed for such measures, although they were seldom put into practice due to judicial hesitance. The new Act restricts nil compensation to specific situations, such as land speculation, abandoned properties, and unused state land. This approach aims to ensure that land serves the greater public interest rather than remaining idle for speculative purposes.
An illustrative case is Muldersdrift in Johannesburg, where luxury estates stand in stark contrast to nearby impoverished informal settlements. Through strategic expropriation, vacant land could be transformed into thriving communities, offering dignity and opportunities to long-marginalized populations. While this would not solve South Africa’s overarching land issues, it would represent a meaningful step forward in promoting equitable growth.
Nevertheless, the path to effective land reform is fraught with obstacles. Outside urban centers, land holds not just economic but also cultural significance. Ownership disputes often reflect deep-rooted community identities, making the issue highly personal. A case in point is a right-wing organization’s attempt to garner international support to block land reform efforts, highlighting the entrenched resistance to change.
Procedural Challenges and Judicial Responsibility
The Expropriation Act, while a potent tool for reform, is not without its procedural challenges. Sections 5-8 provide numerous opportunities for legal objections, potentially delaying expropriation processes. Although these legal frameworks are crafted to ensure fairness, they can become barriers when leveraged by adept attorneys intent on maintaining the status quo. The complexity of these procedures underscores the judiciary’s crucial role in interpreting and applying the law. Courts must demonstrate courage in prioritizing social justice over procedural details, particularly in compensation disputes.
The history of land reform in South Africa serves as a cautionary tale. Despite various policies and initiatives, progress has often been slow, stymied by bureaucratic inefficiencies and resistance from powerful landowners. The success of the Expropriation Act depends on the state’s determination and capability to act decisively. For example, abandoned or hijacked buildings pose significant safety risks, as seen in the tragic Usindiso fire in Johannesburg. Prompt expropriation could prevent such disasters and alleviate housing shortages.
Moving Forward: Beyond Compensation
Ultimately, the discussion surrounding the Expropriation Act should extend beyond the issue of compensation. The real challenge lies in mobilizing state resources and judicial resolve to fulfill the constitutional promise of land reform. South Africa’s past provides valuable lessons on the necessity of bold, decisive action. Just as the Department of Native Affairs once wielded considerable influence, today’s state institutions must demonstrate similar resolve in pursuing fair land distribution.
The path toward reform requires a careful balance of legal expertise and social empathy. As South Africa navigates this intricate terrain, the Expropriation Act stands as both a beacon of hope and a testament to the nation’s dedication to justice and equality. While the journey may be fraught with uncertainty, the need for change is undeniable. The Act is a crucial step in South Africa’s ongoing effort to right historical wrongs and build a more equitable society for future generations.
“`markdown
FAQ: The Expropriation Act of 2024 in South Africa
What is the Expropriation Act of 2024 in South Africa?
The Expropriation Act of 2024 is significant land reform legislation that allows the South African government to expropriate land for the ‘public interest.’ This law aims to address historical injustices and promote equitable land distribution, including provisions for ‘nil compensation’ in certain cases, ensuring that land usage benefits the broader community.
How does the Expropriation Act differ from previous legislation?
The 2024 Act marks a departure from the 1975 Expropriation Act by broadening the grounds for expropriation to include not only ‘public purpose’ but also ‘public interest.’ This change reflects a commitment to social equity and justice, aligning more closely with the principles outlined in South Africa’s Constitution, particularly regarding land reform.
What are the key features of the Expropriation Act of 2024?
One of the key features of the Act is the provision for expropriation with ‘nil compensation’ under certain conditions, such as land speculation, abandoned properties, and unused state land. This approach aims to prevent land from remaining idle and ensure it serves the greater public good.
What challenges does the Expropriation Act face?
The implementation of the Expropriation Act is not without challenges. Procedural complexities may lead to legal objections that can delay expropriation processes. Additionally, the judiciary plays a critical role in interpreting the law, and there may be resistance from landowners and other groups opposed to reform.
How could the Expropriation Act impact communities?
The Act has the potential to transform vacant and underutilized land into thriving communities, addressing socio-economic disparities. For example, in areas like Muldersdrift in Johannesburg, strategic expropriation could provide opportunities and dignity to marginalized populations, although it may not resolve all land-related issues.
What is the broader significance of the Expropriation Act for South Africa’s future?
The Expropriation Act represents a crucial step in addressing historical injustices and promoting equitable land distribution. Its success will depend on the government’s ability to implement the law effectively and mobilize resources to fulfill the constitutional promise of land reform. The Act serves as a beacon of hope for a fairer future in land ownership and social equity.
“`