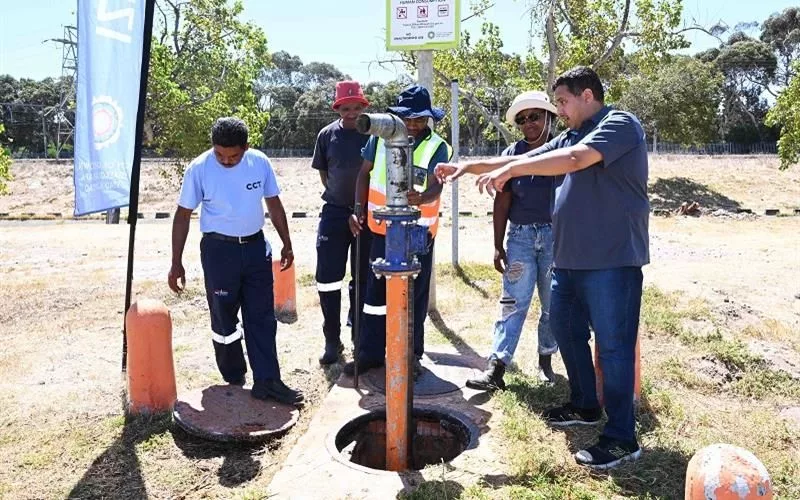
Cape Town is taking bold and proactive steps towards a sustainable water future by promoting the use of treated effluent as a substitute for potable water in non-consumable contexts. With over 330 connections across the city, the treated effluent infrastructure is promoting sustainable and practical water consumption. The city is leading by example, utilizing treated effluent to irrigate its parks and recreational facilities, and is urging various sectors to transition to this resource to contribute towards water conservation.
Cape Town’s Bold Initiative Towards A Sustainable Water Future
Discover the proactive measures taken by the Water and Sanitation Directorate in Cape Town towards a sustainable water future. By leveraging treated effluent as a substitute for potable water in non-consumable contexts, the city is not only benefiting financially but also contributing towards water conservation. With over 330 connections across the city, learn how this treated effluent infrastructure is promoting sustainable and practical water consumption.
The Advent of A Water-Wise Strategy
In response to the global concern of dwindling water resources, the Water and Sanitation Directorate in Cape Town is proactively working towards a sustainable water future. The Directorate is advocating various city sectors – ranging from manufacturing industries, agricultural farms, educational institutions, and even recreational facilities such as parks and golf courses – to leverage treated effluent as a substitute for potable water in non-consumable contexts.
Treated effluent, a purified byproduct of wastewater subjected to extensive cleansing at the Wastewater Treatment Works (WWTW), proves to be a practical alternative for non-consumable purposes such as irrigation, manufacturing, and construction. Transitioning to this resource brings about not only financial benefits via lower water bills but also contributes towards the larger goal of water conservation in Cape Town.
This treated effluent, a product of an intricate process aimed at eliminating impurities, can be safely reintroduced into the natural environment. Presently, the city is proud to produce this from nine WWTWs, conveniently obtainable via 31 draw-off points and nine collection locations spread throughout the city.
Infrastructure for Effluent Distribution
Beyond the mere production of treated effluent, the Water and Sanitation Directorate has also laid a 250-kilometer pipe infrastructure to channel the distribution of treated effluent directly to consumers. With over 330 connections across the city, this network exemplifies the city’s dedication to advocating sustainable water consumption.
Transitioning from tap water to treated effluent for non-drinking purposes is both a financially and environmentally conscious decision. It serves numerous functions such as dust regulation during road construction, maintaining grass fields, and even specific industrial processes. The city itself is leading by example by utilizing treated effluent to irrigate its parks and recreational facilities.
But more than just cost-efficiency and practical applications, opting for treated effluent symbolizes a larger vision. It embodies resilience in future water supply. It represents the adoption of community practices that manage water consumption. And it underscores the role of every individual in preserving our essential water resources.
Promoting the Use of Treated Effluent
To propagate the use of treated effluent, the city ensures easy access through numerous points across the city. Consumers can obtain treated effluent by renting a metered stand-pipe at these draw-off points.
While the cost of utilizing treated effluent fluctuates based on whether the user or the city supplies the infrastructure, the advantages significantly overshadow the investment. For instance, in the case of agricultural irrigation systems that necessitate a minimum of 5 mega litres per day, the city furnishes the required infrastructure.
For those intrigued by this water-wise initiative, the city presents a straightforward application procedure. Users can apply for a temporary or permanent application form by emailing the city’s effluent department. After submitting the completed form and necessary supporting documents, the application is reviewed and the applicant is subsequently notified about the outcome.
However, it is vital to note that treated effluent infrastructure will not be provided to individual residential households to mitigate the risk of cross-connection.
In summary, Cape Town’s endeavors to promote the use of treated effluent are both laudable and crucial. By proposing a sustainable and economically feasible alternative to potable water for non-drinking purposes, the city is spearheading a pioneering move towards a water-wise world. It’s a significant stride towards securing our water resources for the future and a call to action for the rest of the world to follow in these steps.
What is Cape Town’s initiative towards a sustainable water future?
Cape Town is promoting the use of treated effluent as a substitute for potable water in non-consumable contexts to contribute towards water conservation.
What sectors is the Water and Sanitation Directorate urging to transition to treated effluent?
The Water and Sanitation Directorate is urging various city sectors to transition to treated effluent, including manufacturing industries, agricultural farms, educational institutions, and recreational facilities.
What is treated effluent and how is it produced?
Treated effluent is a purified byproduct of wastewater that has undergone extensive cleansing at the Wastewater Treatment Works (WWTW). It is produced through an intricate process aimed at eliminating impurities and can be safely reintroduced into the natural environment.
What is the infrastructure for effluent distribution in Cape Town?
The Water and Sanitation Directorate has laid a 250-kilometer pipe infrastructure to channel the distribution of treated effluent directly to consumers. With over 330 connections across the city, this network exemplifies the city’s dedication to advocating sustainable water consumption.
How can consumers access treated effluent in Cape Town?
Consumers can obtain treated effluent by renting a metered stand-pipe at numerous draw-off points spread throughout the city. Users can apply for a temporary or permanent application form by emailing the city’s effluent department.
Will treated effluent infrastructure be provided to individual residential households?
No, treated effluent infrastructure will not be provided to individual residential households to mitigate the risk of cross-connection.