South Africa’s Expanded Public Works Programme (EPWP) is entering a new era with the announcement of the Khawuleza Model, which aims to create over five million new opportunities and focus on enhancing community infrastructure, developing participant skills, and promoting entrepreneurship. The program will prioritize critical national challenges such as road maintenance, waste management, and energy efficiency projects and aims to foster a self-reliant population capable of making meaningful contributions to South Africa’s social and economic landscape. The government also plans to draw inspiration from successful global initiatives and revitalize workshops to offer practical skills and hands-on experience to participants.
What is the new direction of South Africa’s Expanded Public Works Programme?
South Africa’s government has announced the expansion of the Expanded Public Works Programme (EPWP) to Phase 5, with a new approach called the “Khawuleza Model”. The program aims to create over five million new opportunities and focus on enhancing community infrastructure, developing participant skills, and promoting entrepreneurship. The EPWP will prioritize critical national challenges such as road maintenance, waste management, and energy efficiency projects and foster a self-reliant population capable of making meaningful contributions to South Africa’s social and economic landscape.
A New Direction for the Expanded Public Works Programme
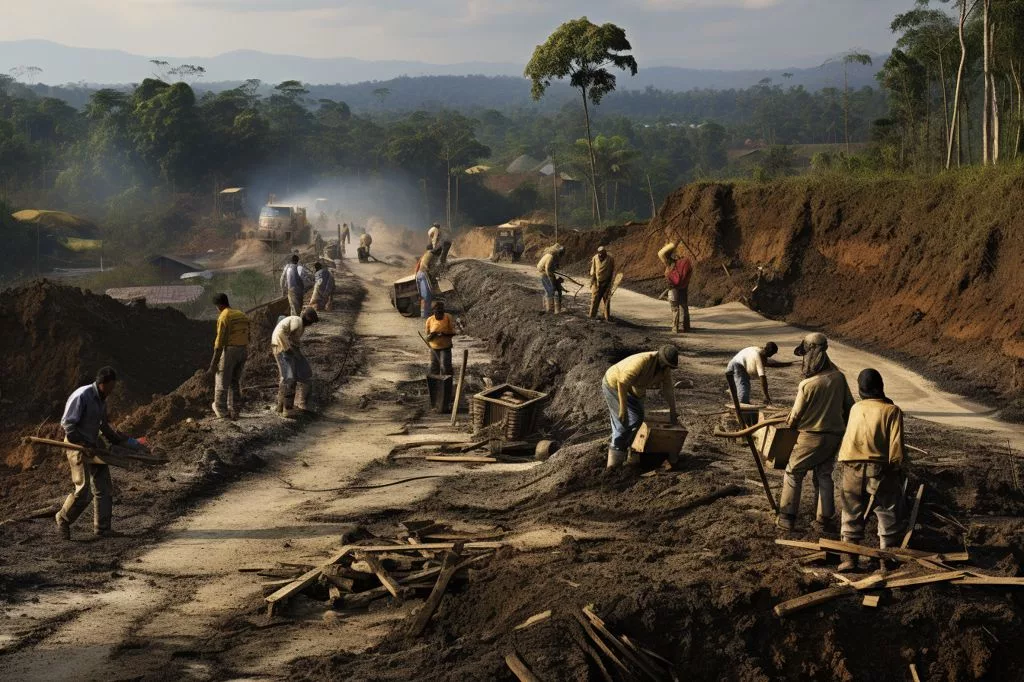
Minister Sihle Zikalala has announced a significant transformation of the Expanded Public Works Programme (EPWP), South Africa’s primary job creation initiative. The program is set to enter Phase 5, with the aim of creating over five million new opportunities, building on the four million generated in Phase 4. This new approach, called the “Khawuleza Model,” will focus on enhancing community infrastructure, developing participant skills, and promoting entrepreneurship.
This shift to Phase 5 comes as the government evaluates the EPWP’s performance and seeks innovative ideas to increase job opportunities for South African youth. Minister Zikalala emphasizes the importance of concentrating on quality rather than quantity. The reimagined EPWP will address critical national challenges, such as road maintenance, waste management, and energy efficiency projects, providing participants with a solid foundation for long-term employment or entrepreneurship.
Revitalizing Workshops and Drawing from Global Successes
Alongside the expanded program scope, the government plans to reopen workshops to offer EPWP participants practical skills and hands-on experience. These rejuvenated facilities will act as centers for innovation and skill development, particularly for graduates of the National Youth Service (NYS). By integrating NYS graduates into these workshops, the government aims to create a culture of ongoing learning and practical application, empowering young people as agents of change.
The revamped EPWP will also be inspired by successful global public employment programs, such as India’s National Rural Employment Guarantee Act and Rwanda’s Umuganda cleaning initiative. These programs provide valuable insight into designing initiatives that improve livelihood security while addressing urgent community needs.
Fostering a Transformational Experience for Participants
Under the Khawuleza Model, the EPWP will place substantial emphasis on training, enterprise development, and creating a transformative experience for participants. The program’s “exit pathways” will ensure that upon completion, participants can secure future employability, self-employment opportunities, or establish organizations that generate additional jobs. Minister Zikalala envisions a future where participants leave the program with confidence, self-reliance, and readiness to contribute to South Africa’s socio-economic landscape.
The EPWP’s new approach aims to change the narrative from despair to hope and growth for South African youth. It will prioritize projects in areas such as road maintenance, energy, waste recycling, and cleaning government buildings as opportunities for innovation, skill development, and environmental stewardship. The government’s commitment to fostering genuine change is apparent in the Khawuleza Model’s acceleration of service delivery and targeted interventions to enhance the living conditions of vulnerable populations.
Cultivating a Skilled and Self-Reliant Populace
The EPWP’s transformation seeks to redefine the program as more than just a means of addressing unemployment. Instead, it aims to develop a skilled, self-reliant population capable of making meaningful contributions to South Africa’s social and economic landscape. As the country’s flagship job creation initiative evolves, the government’s dedication to empowering its youth and building stronger communities is clear, setting the stage for a brighter future.
In conclusion, the South African government’s upcoming overhaul of the Expanded Public Works Programme represents a significant shift in its approach to job creation and youth empowerment. The newly announced Khawuleza Model will focus on enhancing community infrastructure, developing participant skills, and promoting entrepreneurship, drawing lessons from successful global initiatives and broadening the program’s scope to address the country’s most pressing challenges. As the EPWP embarks on this ambitious new chapter, South Africa’s commitment to fostering genuine change and creating lasting opportunities for its youth is more evident than ever.
1. What is the new direction of South Africa’s Expanded Public Works Programme?
The South African government is expanding the Expanded Public Works Programme (EPWP) to Phase 5, with a new approach called the “Khawuleza Model”. The program aims to create over five million new opportunities and focus on enhancing community infrastructure, developing participant skills, and promoting entrepreneurship. The EPWP will prioritize critical national challenges such as road maintenance, waste management, and energy efficiency projects and foster a self-reliant population capable of making meaningful contributions to South Africa’s social and economic landscape.
2. What is the Khawuleza Model?
The Khawuleza Model is a new approach to South Africa’s Expanded Public Works Programme (EPWP) that focuses on enhancing community infrastructure, developing participant skills, and promoting entrepreneurship. The program aims to create over five million new opportunities and prioritize critical national challenges such as road maintenance, waste management, and energy efficiency projects. The goal is to foster a self-reliant population capable of making meaningful contributions to South Africa’s social and economic landscape.
3. What are the priorities of the EPWP under the Khawuleza Model?
Under the Khawuleza Model, the EPWP will prioritize critical national challenges such as road maintenance, waste management, and energy efficiency projects. The goal is to enhance community infrastructure, develop participant skills, and promote entrepreneurship.
4. What is the government’s plan for workshops under the Khawuleza Model?
The government plans to reopen workshops under the Khawuleza Model to offer EPWP participants practical skills and hands-on experience. These rejuvenated facilities will act as centers for innovation and skill development, particularly for graduates of the National Youth Service (NYS). By integrating NYS graduates into these workshops, the government aims to create a culture of ongoing learning and practical application, empowering young people as agents of change.
5. What global public employment programs will the EPWP draw from?
The revamped EPWP will be inspired by successful global public employment programs, such as India’s National Rural Employment Guarantee Act and Rwanda’s Umuganda cleaning initiative. These programs provide valuable insight into designing initiatives that improve livelihood security while addressing urgent community needs.
6. What are the “exit pathways” under the Khawuleza Model?
Under the Khawuleza Model, the EPWP will place substantial emphasis on training, enterprise development, and creating a transformative experience for participants. The program’s “exit pathways” will ensure that upon completion, participants can secure future employability, self-employment opportunities, or establish organizations that generate additional jobs.
7. What is the goal of the EPWP’s new approach?
The EPWP’s new approach aims to change the narrative from despair to hope and growth for South African youth. It will prioritize projects in areas such as road maintenance, energy, waste recycling, and cleaning government buildings as opportunities for innovation, skill development, and environmental stewardship.
8. What is the EPWP’s ultimate goal?
The EPWP’s ultimate goal is to redefine the program as more than just a means of addressing unemployment. Instead, it aims to develop a skilled, self-reliant population capable of making meaningful contributions to South Africa’s social and economic landscape. As the country’s flagship job creation initiative evolves, the government’s dedication to empowering its youth and building stronger communities is clear, setting the stage for a brighter future.