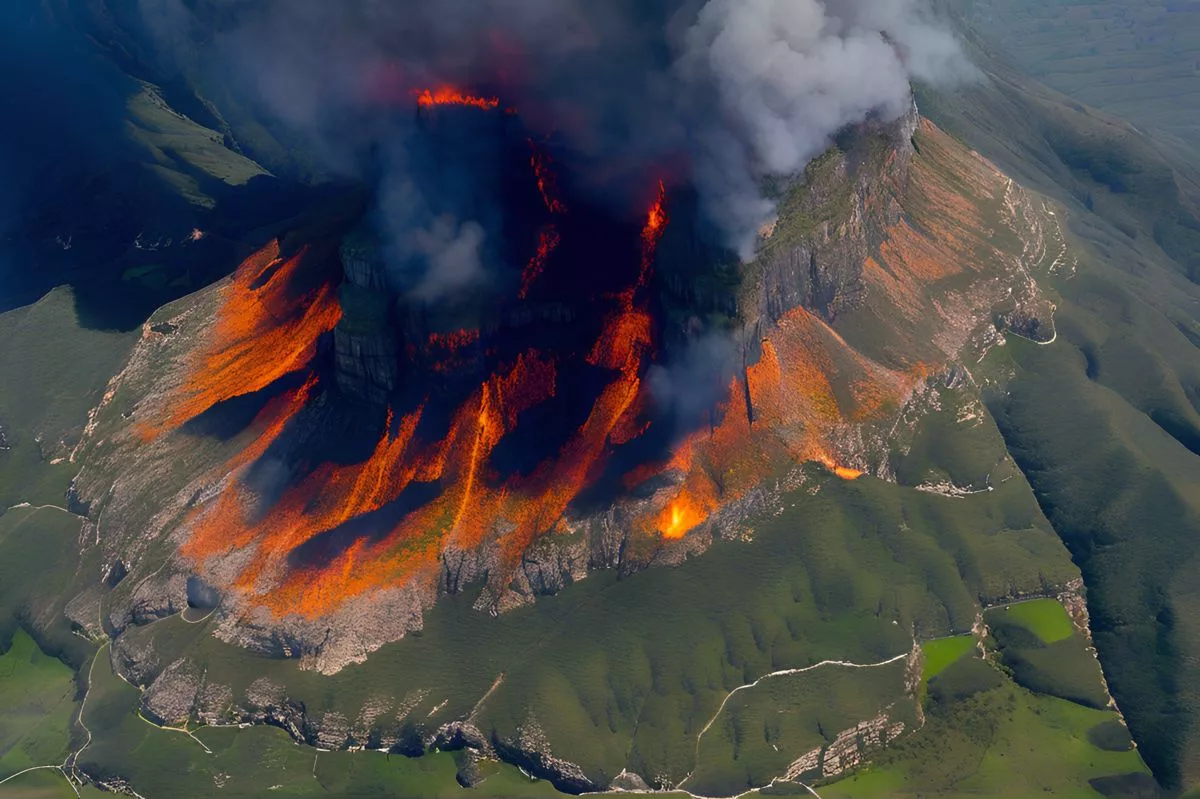
Table Mountain National Park in South Africa uses a fuel reduction burn strategy called stack burning to prevent uncontrolled wildfires. These burns are a calculated precautionary measure that eliminates dry, flammable material that has piled up in the park. TMNP performs these burns every winter to minimize the risk of future destructive fires and to control invasive species. The park is committed to minimizing disruption to households during the process and has recommended precautionary measures for nearby residents. Through strategic prevention, TMNP is protecting South Africa’s rich biodiversity and setting an example of proactive environmental management.
What are Proactive Fire Prevention Measures in Table Mountain National Park?
Table Mountain National Park (TMNP) uses a complex fire management strategy known as fuel reduction burns to mitigate the risk of uncontrolled wildfires. Stack burning, a calculated precautionary measure, is used to incinerate dry, flammable material that has piled up in the park. Every winter, the park performs these fuel reduction burns to eliminate biomass buildup resulting from the clearance of invasive plants. TMNP is committed to taking every possible measure to minimize disruption to households during the preparation and burning operations.
In the heart of South Africa’s captivating natural landscape, Table Mountain National Park (TMNP) is preparing for a vital ecological process known as fuel reduction burns. This complex fire management strategy, set to be carried out during the colder months between July and September, depends on favourable weather conditions.
The TMNP is home to the fire-prone and fire-adaptive fynbos vegetation. The fact that such vegetation is both susceptible to and dependent on fire for its regeneration presents a unique management dilemma.
Intelligent Fire Management in TMNP
As a response to the above challenge, the TMNP has adopted stack burning, a fire control method that, contrary to common belief, is not destructive but rather a calculated precautionary measure. The conditions under which these burns occur are meticulously planned: the temperature must be below 25°C, winds must not exceed 20 km/h, and the burning must commence two to three days after a light rainstorm.
These deliberate fires aim to mitigate the risk of uncontrolled wildfires, which pose a significant threat to human life, property, and the region’s rich biodiversity. By incinerating dry, flammable material that has piled up, the park’s management is proactively reducing the potential for future destructive and uncontrollable wildfires.
Strategic Reduction Burns to Mitigate Wildfire Risk
Every winter, the park performs these fuel reduction burns to eliminate biomass buildup resulting from the clearance of invasive plants. This process is executed strategically; park areas are thoroughly assessed for their risk level and subsequently earmarked for burning.
The purpose of these prescribed and stack burns within the fynbos vegetation is twofold. They reduce fire hazards by eliminating the accumulated ‘fuel’ in the field, a consequence of invasive alien plants, and they form a key component of control operations tasked with eradicating these invasive species.
Several locations within the park have been identified for stack burns, including Cape Point, Tokai Plantation and upper levels, Cecilia (near Kirstenbosch), Newlands, Schotekloof (Cape Town), Sea Point Gum Belt, and Rhodes Memorial.
TMNP’s Commitment to Community Safety and Convenience
In its dedication to the community, the park’s management is committed to taking every possible measure to minimize disruption to households during the preparation and burning operations. Therefore, local residents can rest assured knowing they are in competent and thoughtful hands.
Furthermore, the park management has recommended vital precautionary measures for residents living near the burn sites. These measures include keeping windows closed during the burning, moving flammable items like gas canisters away from outdoor areas, and removing laundry from washing lines to avoid smoke-odour contamination.
In conclusion, the fuel reduction burns conducted by the TMNP serve as a powerful example of how ecological knowledge can be combined with preventative planning to manage and safeguard urban wilderness. This approach not only tackles immediate wildfire threats but also contributes to the broader objective of controlling invasive species, all while conserving the delicate ecological equilibrium of Table Mountain National Park.
Through scrupulous management and strategic prevention, TMNP is guaranteeing the protection of South Africa’s rich biodiversity for future generations. The park’s initiative in managing its unique fire-prone ecosystem serves as a reminder of the importance of proactive and knowledgeable environmental management.
1. What are Proactive Fire Prevention Measures in Table Mountain National Park?
Table Mountain National Park (TMNP) uses a complex fire management strategy known as fuel reduction burns to mitigate the risk of uncontrolled wildfires. Stack burning, a calculated precautionary measure, is used to incinerate dry, flammable material that has piled up in the park. Every winter, the park performs these fuel reduction burns to eliminate biomass buildup resulting from the clearance of invasive plants.
2. What is stack burning?
Stack burning is a fuel reduction burn strategy used by Table Mountain National Park to prevent uncontrolled wildfires. It is a calculated precautionary measure that eliminates dry, flammable material that has piled up in the park. Stack burning is performed every winter to minimize the risk of future destructive fires and to control invasive species.
3. What is the purpose of fuel reduction burns?
The purpose of fuel reduction burns is to reduce the risk of uncontrolled wildfires, which pose a significant threat to human life, property, and the region’s rich biodiversity. By incinerating dry, flammable material that has piled up, the park’s management is proactively reducing the potential for future destructive and uncontrollable wildfires.
4. How does TMNP perform fuel reduction burns?
TMNP performs fuel reduction burns every winter to eliminate biomass buildup resulting from the clearance of invasive plants. This process is executed strategically; park areas are thoroughly assessed for their risk level and subsequently earmarked for burning. The conditions under which these burns occur are meticulously planned: the temperature must be below 25°C, winds must not exceed 20 km/h, and the burning must commence two to three days after a light rainstorm.
5. What is TMNP’s commitment to community safety and convenience during fuel reduction burns?
In its dedication to the community, the park’s management is committed to taking every possible measure to minimize disruption to households during the preparation and burning operations. Therefore, local residents can rest assured knowing they are in competent and thoughtful hands. The park management has also recommended vital precautionary measures for residents living near the burn sites, including keeping windows closed during the burning, moving flammable items like gas canisters away from outdoor areas, and removing laundry from washing lines to avoid smoke-odour contamination.
6. What is the broader objective of fuel reduction burns?
The broader objective of fuel reduction burns is to control invasive species, all while conserving the delicate ecological equilibrium of Table Mountain National Park. Through scrupulous management and strategic prevention, TMNP is guaranteeing the protection of South Africa’s rich biodiversity for future generations. The park’s initiative in managing its unique fire-prone ecosystem serves as a reminder of the importance of proactive and knowledgeable environmental management.