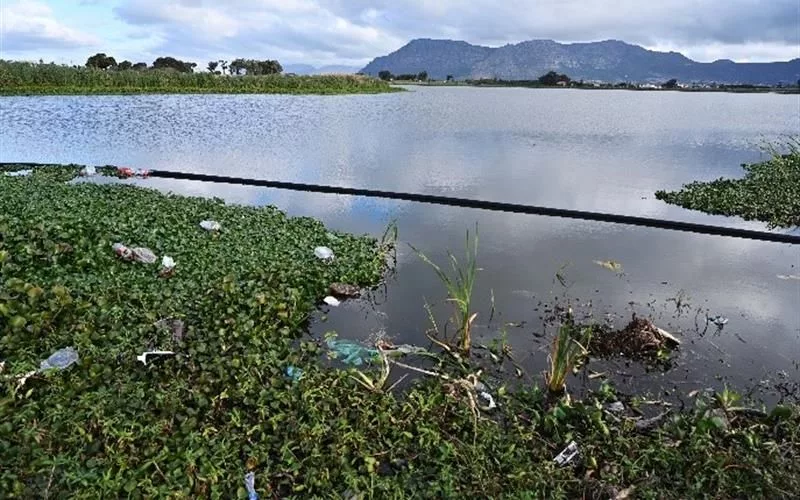
Waste interceptors are cost-efficient tools that trap floating rubbish and debris in urban aquatic channels, ensuring a cleaner and healthier ecosystem. The city of Cape Town has successfully installed eight waste interceptors in rivers and water channels, showcasing its dedication to environmental conservation. The interceptors are designed using a simple mechanism and are adaptable to a range of waterways, making them an effective solution for litter control. The city’s continued commitment to maintaining and cleaning the interceptors highlights its resolve to improve water quality and safeguard long-term ecosystem health.
What is the role of waste interceptors in aquatic channels?
Waste interceptors serve as guardians of urban aquatic channels by trapping floating rubbish and debris before they can be carried downstream or into larger water bodies. They are cost-efficient and adaptable tools that provide a more economical option for litter control compared to complex filtration or cleaning systems. The city of Cape Town has successfully installed eight waste interceptors in rivers and water channels, demonstrating its commitment to preserving aquatic channels and ecosystems for the benefit of future generations.
The Birth of a Sustainable City
The urban landscape is constantly evolving, crafting a compelling narrative that integrates revolutionary methods to combat water contamination. A significant milestone was reached in the fiscal year of 2023/2024 when eight waste interceptors were successfully installed in rivers and water channels throughout this dynamic city.
This brilliant endeavor, a balance of economic wisdom and ecological guardianship, was realized through cost-efficient procedures designed to trap litter and prevent waste, thus safeguarding our delicate ecosystem. The Water and Sanitation, Catchment Stormwater and River Management (CSRM) Branch, a pivotal protagonist in this transformation, invested a hefty R238,000 to install these waste interceptors. Rooted firmly in Southfield’s Princess Vlei, Garden Village’s Black River, Pinelands’ Elsieskraal River, and Athlone’s Jakkalsvlei Canal, these interceptors serve as guardians of urban aquatic channels.
The Ingenious Mechanism
The workings of the system reveal a beautifully straightforward design: a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe with a diameter of 75mm is attached to each side of the water body. These interceptors, in harmony with the measurements of the water body, have lengths that vary, with some reaching an impressive 90 meters.
The benefits provided by waste interceptors are manifold. Primarily, they act as sieves, trapping floating rubbish and debris before they can be carried downstream or into larger water bodies. They provide a more economical option for litter control compared to complex filtration or cleaning systems. Furthermore, their flexibility to accommodate an array of waterways renders them an extremely adaptable tool.
Examples of Successful Implementation
A notable example of an interceptor installation can be found at Princess Vlei, where three interceptors are part of a wetland system extending from Grassy Park to Strandfontein. The Southfield Canal, about 2km in length, boldly discharges into Princess Vlei, draining a considerable urban zone of approximately 800 hectares. The vlei, meanwhile, collects runoff from several public open spaces and stormwater pipes, including those from Wynberg, Youngsfield, Plumstead, and Southfield. This accumulated water subsequently passes through an outlet weir before flowing south-eastward into the Italian Road Canal, and eventually reaching Rondevlei in Grassy Park.
Continued Commitment to Conservation
The city’s pledge to environmental conservation extends to the routine cleaning and maintenance of all waste interceptors. Adding a further dimension to this plan, Princess Vlei additionally experiences annual hydraulic flushing during the wet winter months.
This unwavering commitment was underscored by Councillor Zahid Badroodien, the City’s Mayoral Committee Member for Water and Sanitation. He reiterated the Water and Sanitation Directorate’s resolve to improve the water quality in rivers and waterways. In his view, the installation of these waste interceptors significantly boosts their ability to remove solid waste from the waterways, safeguarding the long-term health of our ecosystems.
The Future of Urban Development
In this continued journey, the city has demonstrated its prowess as a savvy navigator, plotting a path defined by environmental accountability and inventive solutions. The placement of waste interceptors in rivers and water channels stands as a testament to this dedication, a salute to the city’s commitment to preserving our aquatic channels and ecosystems for the benefit of future generations.
How do waste interceptors work in aquatic channels?
Waste interceptors are simple mechanisms that serve as sieves, trapping floating rubbish and debris before they can be carried downstream or into larger water bodies. They are attached to each side of the water body using a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe with a diameter of 75mm and vary in length depending on the size of the waterway.
What are the benefits of waste interceptors?
Waste interceptors provide a cost-efficient and adaptable solution for litter control in urban aquatic channels, ensuring a cleaner and healthier ecosystem. They are easier to install than complex filtration or cleaning systems and are flexible enough to accommodate a range of waterways.
Where have waste interceptors been successfully installed in Cape Town?
The city of Cape Town has successfully installed eight waste interceptors in rivers and water channels, including Southfield’s Princess Vlei, Garden Village’s Black River, Pinelands’ Elsieskraal River, and Athlone’s Jakkalsvlei Canal.
How does Cape Town maintain and clean the waste interceptors?
The city of Cape Town is committed to the routine cleaning and maintenance of all waste interceptors, ensuring their continued effectiveness. Princess Vlei experiences annual hydraulic flushing during the wet winter months, adding another dimension to the plan.
What is the city’s commitment to environmental conservation?
The city of Cape Town has demonstrated a continued commitment to environmental conservation by installing waste interceptors in rivers and water channels, and by pledging to improve water quality and safeguard the long-term health of ecosystems.
What does the installation of waste interceptors represent for the future of urban development?
The placement of waste interceptors in rivers and water channels represents the city’s dedication to preserving our aquatic channels and ecosystems for the benefit of future generations. It demonstrates the city’s ability to navigate environmental accountability and develop inventive solutions for a sustainable future.