Sudan is on the brink of a civil war as the conflict between the head of Sudan’s Armed Forces, General Abdelfatah El-Burhan, and the head of the Rapid Support Forces, Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, continues to escalate. This crisis poses severe challenges for those attempting to deliver humanitarian aid in the region, leading to a significant increase in refugees fleeing to neighboring countries.
The Refugee Situation in Sudan
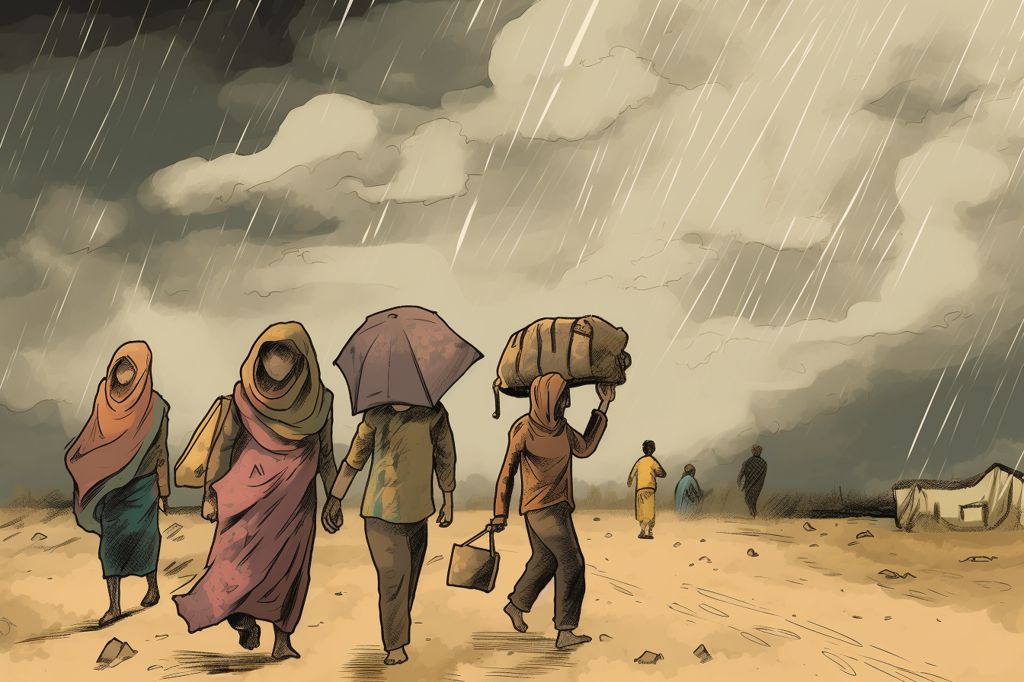
The refugee situation in Sudan is particularly distressing due to the number of people affected. As the conflict intensifies, at least 100,000 individuals have sought refuge in nearby countries such as Chad, Egypt, and South Sudan. Before the current crisis, Sudan was home to 1.1 million refugees, making it one of Africa’s largest refugee host countries.
Obstacles to Humanitarian Aid
Humanitarian aid efforts face numerous obstacles as the conflict continues to rage. Providing essential resources to those in desperate need remains a daunting challenge due to ongoing insecurity. Furthermore, Sudanese aid groups requested nearly $2 billion in 2021, but only half of this amount was funded by donors, leaving a significant financial shortfall for current relief missions.
International Response
The United Nations, the European Union, and a few individual countries have primarily led the international response to the Sudanese crisis. The African Union has condemned the violence and called for an immediate humanitarian ceasefire while pledging to coordinate international action in Sudan. Global organizations such as UNHCR, International Medical Corps, UNICEF, and UN Women have initiated regional refugee emergency responses. The European Union has allocated €200,000 (approximately US$220,000) for immediate relief, and first aid assistance, and the Arab League is holding emergency meetings to resolve the conflict.
Actions Needed
To address the root causes of the refugee crisis and mitigate the unfolding humanitarian disaster, a peace agreement must be reached in Sudan. Until that becomes a reality, the rights of refugees, asylum-seekers, and returnees must be respected and protected under international law. In addition, countries receiving refugees must adhere to the principle of non-refoulment, ensuring that people are not forced to return to dangerous situations in their home countries.
Improved security analysis and coordination mechanisms between civilian and military actors are crucial in addressing the crisis. Lastly, funding for relief efforts must be significantly increased, with donor countries working collaboratively to ensure accountability and prioritize the needs of those affected by this alarming humanitarian situation.
It is only through a concerted, global effort that the crisis in Sudan can be effectively managed, and the lives of countless innocent civilians can be protected.