The Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) in Cape Town is undergoing an exciting transformation with the release of the Local Spatial Development Framework (LSDF). The LSDF integrates urban design, environmental conservation, and economic growth, and residents can shape the plan by attending open house meetings, providing feedback online or via email, and reviewing hard copies of the plan before the March 22nd deadline. The LSDF represents a collaborative effort to create sustainable growth and preservation in the GBDA, creating a vibrant and sustainable future for the community.
How can residents participate in shaping the Gordon’s Bay Development Area Master Plan?
Residents can participate in shaping the Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) Master Plan by attending open house meetings on February 24th and March 8th, submitting feedback through the City of Cape Town’s online portal or email address, and reviewing hard copies of the plan at the Subcouncil 8 office and Gordon’s Bay Library before the deadline on March 22nd, 2024. The LSDF for the GBDA represents a community united in shaping their common future through dialogue and cooperation.
20th February 2024
Section 1: The GBDA’s Promise and Potential
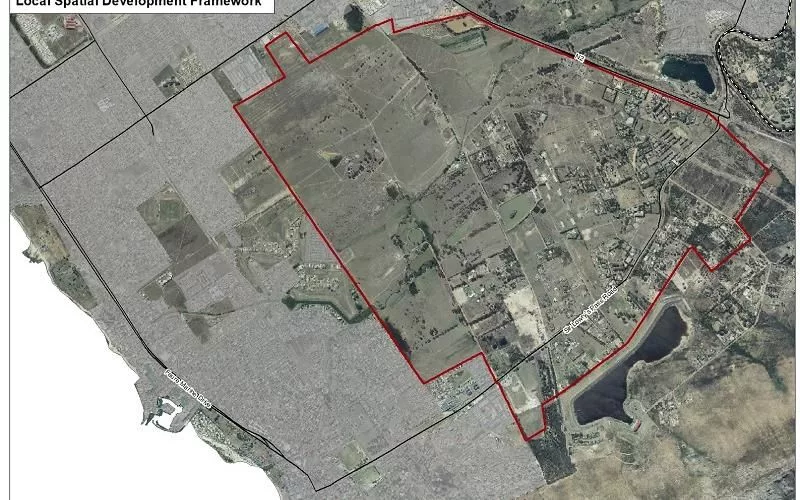
Cape Town is on the verge of a remarkable metamorphosis. The pivotal point of this change is the Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA). This vital swath of land stretches between the N2 highway and the eastern edge of Sir Lowry’s Pass Road. Nestled to the north of the coastal town, the GBDA offers a fantastic opportunity for sustainable urban expansion.
This vast mosaic of vacant and underused plots is currently the focus of an exhaustive planning scheme known as the Local Spatial Development Framework (LSDF). The preliminary LSDF, released to the public on 24th January 2024, sketches out a future roadmap for the GBDA. This concept integrates urban design, environmental conservation, and economic progression, all founded on the unique aspects of the area.
However, the onus of spearheading this initiative doesn’t solely rest on urban planners and architects. The City of Cape Town encourages all key players, including residents and entrepreneurs, to actively participate in shaping the GBDA’s destiny. Their viewpoints are critical to the project’s success.
Section 2: Encouraging Community Participation
To encourage this dialogue, the City has planned two open house meetings, which will serve as platforms for inquiries, discussions, and insights about the draft LSDF. The meetings are slated for Saturday, 24 February, and Friday, 8 March at the Charles Morkel Community Hall in Strand. City officials will be in attendance to steer the conversation and explain the intricate process of spatial planning.
Eddie Andrews, the City’s Deputy Mayor and Mayoral Committee Member for Spatial Planning and Environment, calls on residents to leverage this chance. “This is the perfect time to ask questions and understand the process we are using to develop the spatial vision for this area,” he commented.
Moreover, there are multiple ways to contribute for those who cannot attend the meetings. The City of Cape Town has set up various platforms for input, including an online portal on the City’s website, an email address for comments on the draft LSDF, and hard copies of the plan at the Subcouncil 8 office and Gordon’s Bay Library. All submissions should be made before the deadline on 22nd March 2024.
Section 3: The LSDF as a Policy Tool and the GBDA’s Developmental Balance
At its essence, the LSDF functions as a policy tool. It outlines the developmental path for an area, merging the community’s aspirations. It thereby acts as a reference, impacting decisions on land use and development applications.
The GBDA, with its vast developmental potential, exemplifies the delicate equilibrium between progress and conservation. Alderman Andrews succinctly encapsulates this view: “While it’s crucial to develop to accommodate population growth demands, it must be managed sustainably to uphold and safeguard the unique characteristics of the area.”
Section 4: The Collaborative Ethos and the Integrated Approach
This initiative is based on a cooperative philosophy. The draft LSDF, once fine-tuned with public feedback, will be submitted to the Council for ratification. The journey to the final LSDF is thus studded with the collective ambitions of a community, each step forward reflecting the communal vision for the GBDA.
The LSDF for the GBDA is not an isolated plan. It adheres to the spatial development guidelines outlined in the Helderberg District Spatial Development Framework, a regional plan for the larger Helderberg area. It thus represents an integrated approach to planning, ensuring the GBDA’s future seamlessly fits into the broader urban context.
Section 5: More Than Just a Plan
Beyond being an urban development scheme, the LSDF for the GBDA symbolizes a community uniting to shape their common future through dialogue and cooperation. It affirms the belief that sustainable growth and preservation can coexist, creating an urban landscape that respects both the past and the future. Thus, the narrative of the GBDA unfolds as a story of a city and its people, charting their path towards a vibrant, sustainable future.
1. How is the Gordon’s Bay Development Area undergoing transformation?
The Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) in Cape Town is undergoing transformation through the release of the Local Spatial Development Framework (LSDF), which integrates urban design, environmental conservation, and economic growth.
2. How can residents participate in shaping the Gordon’s Bay Development Area Master Plan?
Residents can participate in shaping the Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) Master Plan by attending open house meetings, submitting feedback through the City of Cape Town’s online portal or email address, and reviewing hard copies of the plan before the deadline on March 22nd, 2024.
3. What is the Local Spatial Development Framework (LSDF)?
The Local Spatial Development Framework (LSDF) functions as a policy tool that outlines the developmental path for an area, merging the community’s aspirations. It impacts decisions on land use and development applications in the GBDA.
4. What is the collaborative ethos behind the Gordon’s Bay Development Area Master Plan?
The Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) Master Plan is based on a cooperative philosophy, with the LSDF being fine-tuned with public feedback and submitted to the Council for ratification. The LSDF also adheres to the spatial development guidelines outlined in the Helderberg District Spatial Development Framework, representing an integrated approach to planning.
5. What does the Gordon’s Bay Development Area Master Plan symbolize?
Beyond being an urban development scheme, the Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) Master Plan symbolizes a community uniting to shape their common future through dialogue and cooperation, creating a sustainable and vibrant future for the GBDA.
6. Who should participate in shaping the Gordon’s Bay Development Area Master Plan?
All key players, including residents and entrepreneurs, are encouraged to actively participate in shaping the Gordon’s Bay Development Area (GBDA) Master Plan, as their viewpoints are critical to the project’s success.