South Africa’s biodiversity is threatened by invasive species, which have been introduced into various ecosystems and have caused extensive damage to water assets, pastures, and native biodiversity. The introduction of 32 new alien species in the past decade has worsened the risks associated with wildfires and flooding, making it a monumental challenge that requires a concerted and cooperative effort from all stakeholders. The government has pledged over 1.5 billion Rand to tackle biological invasions, and NGOs have secured over 180 million Rand to control invasive species in water catchments around Cape Town. Nevertheless, the challenge ahead remains monumental and requires unity and collaboration from all stakeholders.
What are the threats to South Africa’s biodiversity?
South Africa’s biodiversity is threatened by invasive species that infest various ecosystems, overshadow native species, and disrupt crucial ecological processes. The introduction of 32 new alien species in the past decade has caused extensive damage to South Africa’s water assets, pastures, and the native biodiversity. Invasive species can also worsen the risks associated with wildfires and flooding, making the fight against biological invasions a monumental challenge that requires a concerted and cooperative effort from all stakeholders.
As the radiant African sun graces the heavens, Barbara Creecy, South Africa’s Minister of Forestry, Fisheries, and the Environment, takes her position at the Pretoria National Botanical Gardens’ lectern. The gathering before her is an assortment of government officials, researchers, scientists, and distinguished contributors all eagerly waiting for the unveiling of the 3rd National Status of Biological Invasives and their Management report.
Creecy unveils this scientific research report as a key tool in the fight against South Africa’s invasive species predicament, an issue that stretches beyond just biodiversity. She underscores that these invasive species pose a significant risk as they infest various ecosystems, overshadow native species, and disrupt crucial ecological processes.
The Pervasive Impact of Invasive Species
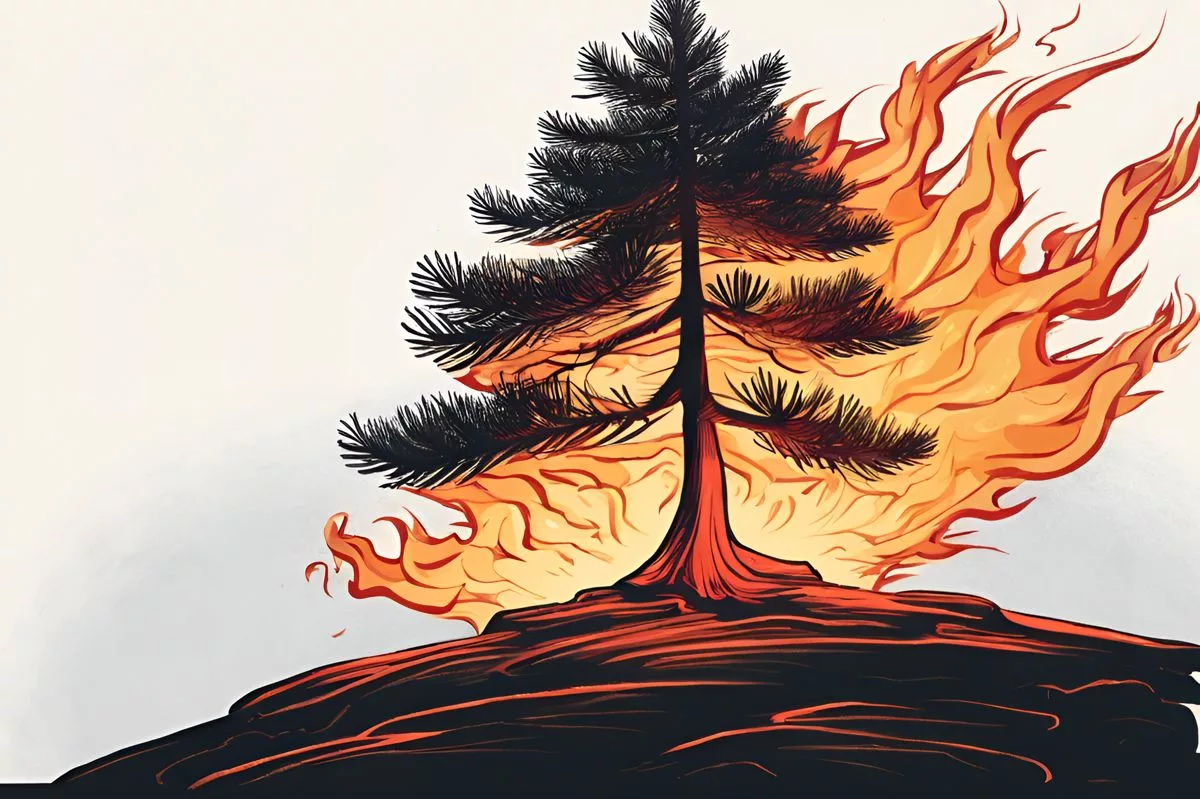
A closer examination of the report reveals the disconcerting nature of the situation at hand. The past decade has seen the introduction of 32 new alien species into the naturally existing ecosystems. Both alien freshwater fishes and invasive trees have caused extensive damage to South Africa’s water assets, pastures, and the native biodiversity. A striking instance of this is the unexpected invasion of pine trees into mountain catchments, which leads to excessive water consumption, heightened fire intensity, and a reduction in indigenous biodiversity.
Furthermore, the distinctive and vulnerable biodiversity of the Prince Edward Islands is under attack. Marion Island is home to 44 alien species, with over half categorized as invasive. On Prince Edward Island, every one of the eight alien species is deemed invasive. These invasions present a significant and immediate risk to the unique biodiversity of these islands.
Invasive Species and Climate Change
In a world increasingly concerned with climate change and global warming, the presence of invasive species can potentially worsen the risks associated with wildfires and flooding. Pine trees, for instance, are highly flammable. Other invasive varieties can block natural waterways that typically alleviate the effects of floods and cyclones.
However, the unveiling of these issues is not a cause for despair but rather a rallying cry for action. With South Africa leading the charge in invasion science, the nation remains resolute in its commitment to tackle these challenges head-on.
The Fight Against Biological Invasions
Between 2020 and 2022, the government has pledged over 1.5 billion Rand to address biological invasions. This funding targets priority regions such as strategic water source areas, protected areas, and biodiversity hotspots. Additionally, NGOs have managed to secure over 180 million Rand from private sectors to control invasive freshwater fishes and alien plants in the water catchments around Cape Town.
There are also concrete plans to tackle the biological invasions on the Prince Edward Islands. An ambitious plan to eliminate the destructive house mice from Marion Island is underway. This project is vital as these mice feed on plants, invertebrates, and endangered seabirds, posing a significant threat to the island’s unique biodiversity.
Nevertheless, the challenge that lies ahead is monumental. The problem of biological invasions requires a concerted and cooperative effort from all stakeholders. This includes the government, academic institutions, civil society organizations, and local communities. They must pool resources to enhance prevention measures, early detection, and control strategies while continuing to invest in research and innovation.
In conclusion, Minister Creecy calls for unity and collaboration in addressing this looming challenge. She implores all stakeholders to heed the report’s findings and commit to tackling the problems associated with biological invasions. Only by doing so can South Africa safeguard its status as a sanctuary for its treasured indigenous plants, animals, and ecosystems that support sustainable development and human well-being.
What is the government doing to tackle biological invasions in South Africa?
The government has pledged over 1.5 billion Rand to tackle biological invasions in South Africa. The funding targets priority regions such as strategic water source areas, protected areas, and biodiversity hotspots. Additionally, there are concrete plans to tackle biological invasions on the Prince Edward Islands, including an ambitious project to eliminate house mice from Marion Island, which pose a significant threat to the island’s unique biodiversity.
Why are invasive species a threat to South Africa’s biodiversity?
Invasive species are a threat to South Africa’s biodiversity as they infest various ecosystems, overshadow native species, and disrupt crucial ecological processes. The introduction of 32 new alien species in the past decade has caused extensive damage to water assets, pastures, and the native biodiversity. Invasive species can also worsen the risks associated with wildfires and flooding.
How are NGOs contributing to controlling invasive species in South Africa?
NGOs have secured over 180 million Rand to control invasive species in water catchments around Cape Town. This funding targets controlling invasive freshwater fishes and alien plants.
What is the impact of invasive species on the Prince Edward Islands?
The distinctive and vulnerable biodiversity of the Prince Edward Islands is under attack. Marion Island is home to 44 alien species, with over half categorized as invasive. On Prince Edward Island, every one of the eight alien species is deemed invasive. These invasions present a significant and immediate risk to the unique biodiversity of these islands.
How can South Africa tackle the challenge of biological invasions?
Tackling the challenge of biological invasions requires a concerted and cooperative effort from all stakeholders. This includes the government, academic institutions, civil society organizations, and local communities. They must pool resources to enhance prevention measures, early detection, and control strategies while continuing to invest in research and innovation.
What are the risks associated with invasive species and climate change?
Invasive species can potentially worsen the risks associated with wildfires and flooding. Pine trees, for instance, are highly flammable. Other invasive varieties can block natural waterways that typically alleviate the effects of floods and cyclones.