A report from the Office of the Public Protector has revealed the poor assistance provided to victims of gender-based violence (GBV) by South African authorities, including the police service and departments of social development and justice. The investigation was triggered by the tragic death of Altecia Kortje and her daughter after Kortje was dismissed when seeking a protection order. The report found dilapidated court buildings, malfunctioning equipment, a lack of victim-friendly spaces, and deficiencies in the GBV support initiatives. The Public Protector has recommended training for the police service and detailed project plans from all departments to address these concerns.
Unveiling the Hardships Faced by GBV Victims: A Deep Dive into South African Authorities. The Office of the Public Protector has recently released an alarming report, showcasing the unsatisfactory assistance provided to victims of gender-based violence (GBV) by the South African Police Service (SAPS) along with the Departments of Social Development, and Justice and Constitutional Development.
The Public Protector’s Damning Revelation
The Office of the Public Protector has recently released an alarming report, showcasing the unsatisfactory assistance provided to victims of gender-based violence (GBV) by the South African Police Service (SAPS) along with the Departments of Social Development, and Justice and Constitutional Development. The thorough investigation, triggered by the distressing dismissal of Altecia Kortje at the Bellville Magistrate’s Court in June 2020 when she sought a protection order, scrutinized 38 magistrates’ courts throughout the nation. In a heartbreaking turn of events, Kortje and her daughter met with a tragic death post their dismissal.
This somber incident sparked Deputy Minister of Justice, John Jeffreys, into action, instigating the Public Protector, Advocate Kholeka Gcaleka, to probe the administrative challenges experienced by GBV victims within the folds of the criminal justice system. Gcaleka’s findings painted an austere picture of under-provision, deteriorating infrastructures, and malfunctioning equipment within the Department of Justice and Constitutional Development.
Dire Conditions at Magistrates’ Courts
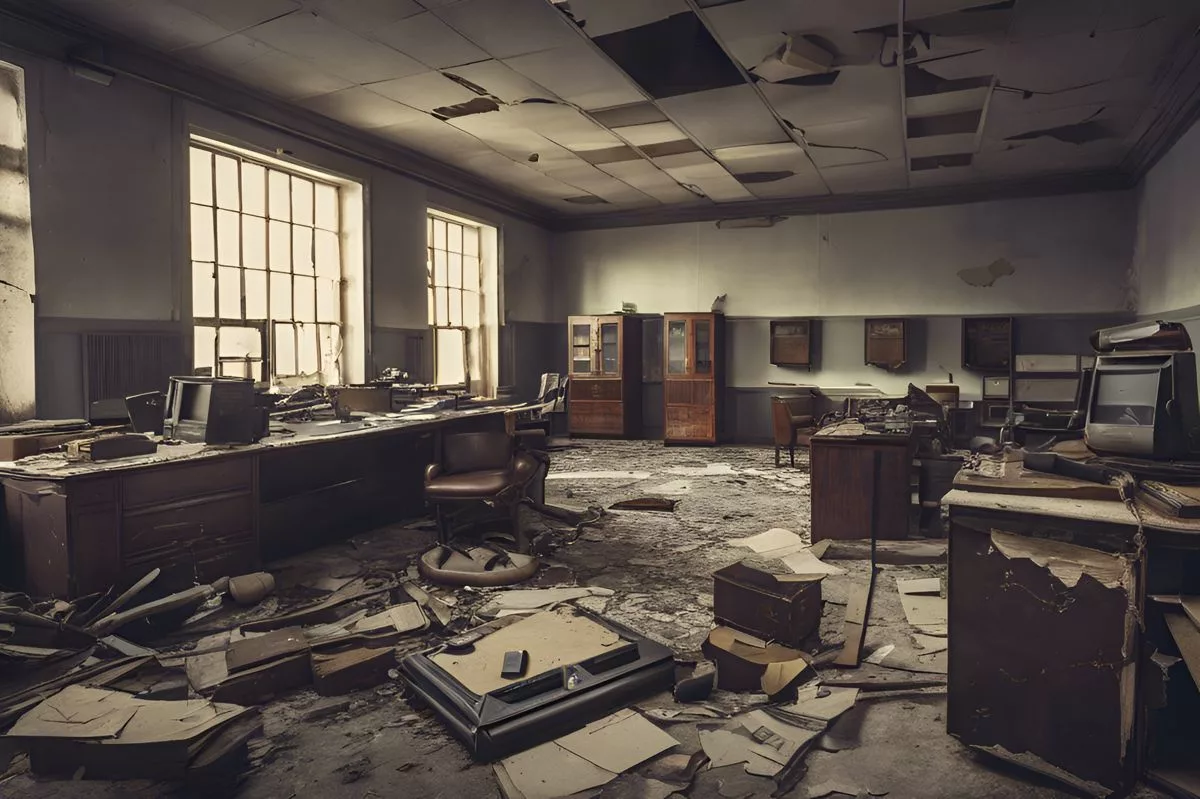
In a striking discovery, several amongst the 38 court locations analyzed were found to be antiquated and in a state of disrepair. Vital office devices were insufficient and malfunctional, including problematic telephone lines, air conditioners, switchboards, and enduring network issues. Alarming deficiencies were noted in the Integrated Case Management Systems (ICMS), making them mostly unreachable or frustratingly slow. These major drawbacks were visible in the Umlazi, Umbumbulu, Mamelodi, Mzumbe, and Ndwendwe Magistrates Courts.
The circumstances for victims were equally bleak. There was a significant dearth of private consultation rooms for victims in the courts, and most lacked suitable filing systems or spaces. The sight of files randomly scattered across the floor in Mamelodi, Pretoria, Palm Ridge, Vereeniging, Johannesburg, and Bellville was disheartening, with some even found in police cells at Ga-Rankuwa.
Gcaleka has now tasked the Department of Justice to present a comprehensive project plan detailing improvements to buildings and ICT, along with renovations to court structures, within a span of seven months.
Shortcomings of SAPS and DSD
The SAPS also faced a similar critique for their deficient approaches in handling GBV incidents. Victim-friendly spaces were notably absent in numerous police stations, particularly in rural regions. The lack of such provisions force victims into overcrowded police stations, a situation that inevitably exacerbates their existing trauma. Worryingly, certain SAPS officers showed reluctance in registering cases, thereby depriving victims the right to initiate criminal proceedings.
Consequently, Gacleka has recommended that SAPS undertake training within six months, focusing on gender sensitivity, GBV awareness, and practical application of the Domestic Violence Act.
The Department of Social Development (DSD) was also brought under scrutiny for its scarcity of shelters for GBV victims. The department’s crucial support initiatives, namely the Gender-Based Violence Command Centre and the Everyday Heroes Programme, were found to be understaffed. Furthermore, an apparent lack of collaboration between the DSD and SAPS in providing supportive services to GBV victims was noted.
Gcaleka has now insisted that the DSD present a detailed project plan within six months to address these concerns and formulate a plan with definitive timelines.
The Road Ahead
Addressing the Kortje family, Gcaleka stated, “we acknowledge that this report will not return your daughter, mother, or sister. However, the path she treaded to this very court was not fruitless. It has aided many GBV victims by drawing attention to their struggle”. Jeffreys echoed these sentiments, confirming that the Department welcomes the findings and plans to execute the remedial measures detailed in the report.
What is the Office of the Public Protector report about?
The report reveals the poor assistance provided to victims of gender-based violence (GBV) by South African authorities, including the police service and departments of social development and justice. The investigation was triggered by the tragic death of Altecia Kortje and her daughter after Kortje was dismissed when seeking a protection order.
What were the major issues found in the magistrates’ courts?
Several court locations analyzed were found to be antiquated and in a state of disrepair. Vital office devices were insufficient and malfunctional, including problematic telephone lines, air conditioners, switchboards, and enduring network issues. Deficiencies were noted in the Integrated Case Management Systems (ICMS), making them mostly unreachable or frustratingly slow. These major drawbacks were visible in the Umlazi, Umbumbulu, Mamelodi, Mzumbe, and Ndwendwe Magistrates Courts.
What were the shortcomings of the SAPS and DSD?
The SAPS faced critique for their deficient approaches in handling GBV incidents. Victim-friendly spaces were notably absent in numerous police stations, particularly in rural regions. Certain SAPS officers showed reluctance in registering cases, thereby depriving victims the right to initiate criminal proceedings. The DSD was brought under scrutiny for its scarcity of shelters for GBV victims. The department’s crucial support initiatives, namely the Gender-Based Violence Command Centre and the Everyday Heroes Programme, were found to be understaffed.
What are the recommendations made by the Public Protector?
The Public Protector has recommended training for the police service and detailed project plans from all departments to address the concerns found during the investigation. The Department of Justice has been tasked with presenting a comprehensive project plan detailing improvements to buildings and ICT, along with renovations to court structures, within a span of seven months. SAPS has been recommended to undertake training within six months, focusing on gender sensitivity, GBV awareness, and practical application of the Domestic Violence Act. The DSD has been asked to present a detailed project plan within six months to address the concerns found during the investigation and formulate a plan with definitive timelines.
What is the Department of Justice doing to address the concerns?
The Department of Justice has plans to execute the remedial measures detailed in the report, including presenting a comprehensive project plan detailing improvements to buildings and ICT, along with renovations to court structures, within a span of seven months.
What is the impact of the report on GBV victims?
The report has drawn attention to the struggles of GBV victims in South Africa and has highlighted areas where improvements are needed. While it may not be able to return victims who have lost their lives, it has aided many GBV victims by drawing attention to their struggle. The Department of Justice has welcomed the findings and plans to execute the remedial measures detailed in the report.